SpaceX vs ISRO – What makes SpaceX and ISRO stand out? Space is vast and fascinating but space exploration is tedious and highly expensive. Nevertheless, it has become a proxy contest among countries to show their power. Future space exploration aims to fly farther from Earth than ever before. Agencies like NASA, RSA (aka Roscosmos), and ESA have been in the industry for a long time now. Despite having multi-dollar funding, these agencies have been trying hard for decades to make their stand steady. In comparison, the ISRO and SpaceX seem to be young, but their entries resulted in major breakthroughs in the Space Industry. Let’s take a deeper into these two.
SpaceX vs ISRO – What makes SpaceX and ISRO stand out FROM OTHER AGENCIES?
India’s ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is the space agency of the Government of India and has its headquarters in the city of Bengaluru. Its vision is to “harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research & planetary exploration”. The committee Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by Jawaharlal Nehru under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962. It all started with the urging of scientist Vikram Sarabhai recognising the need in space research. Later, in 1972, the Government of India had set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS). Now the ISRO is under the Department of Space, which directly reports to the Prime Minister of India. (source-Wikipedia)
Elon Musk’s SpaceX
In 2001, Musk came up with a concept called ‘Mars Oasis’. A project to bring the mars travel into reality and to grow plants on Mars soil. He, along with friends, travelled to Moscow, Russia to look for some launch vehicles which could take them to space. They were offered a deal for $8 – $10 million for a rocket, which Musk considered too expensive which he couldn’t afford at that time. While coming from Moscow, he thought of creating his own company to make affordable rockets and other pieces of equipment in order to reduce the overall cost of space exploration. And, thus, SpaceX became a reality.
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., trading as SpaceX, is an American aerospace manufacturer and space transportation services company headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the goal of reducing space transportation costs to enable the colonization of Mars. SpaceX has developed several launch vehicles, the Starlink satellite constellation, and the Dragon spacecraft. (source-Wikipedia)
Also Read – From Zip2 to SpaceX: All about Elon Musk companies
OTHER ARTICLES YOU MIGHT LIKE TO READ
Similarities
Struggle in the beginning
- ISRO – 1960 – 1980s were the times when all three prominent agencies (NASA, ROSCOSMOS, and ESA) were fighting to make their best foot in space exploration. And that’s when ISRO entered into the space game by successfully launching their first satellite, Aryabhata, by the Soviet Union on April 19, 1975. However, their failure on SLV in 1979 followed by the failure on ASLV in 1987 gave a slight downfall in their space mission. In the meantime, Glavkosmos a subsidiary of Roscosmos halted the transfer of the associated manufacturing and design technology to India. Until then, ISRO had not been affected by technology transfer restrictions. Learning from all the failures, ISRO decided to stand on their own. The cost-efficiency and the result-oriented approach paid off with huge success. ISRO’s successful launch of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) in 1994 and the Geostationary Space Launch Vehicle (GSLV) in 2004 -2010 considered as ISRO’s remarkable achievements.
- SpaceX – Musk invested a lot of money which he got from the sale of PayPal into SpaceX. The much-awaited first SpaceX launch in 2006 failed in just 33 seconds after lift-off because of a rusty nut. The second one in 2007 also failed because of the engine, which shut down prematurely and the rocket failed to reach orbit. Later, they managed to get their first contract with NASA which also ended up in a failure. The satellite which was supposed to be placed in the orbit landed in the sea. However, the fourth launch in 2008 was a huge success, and as a result, SpaceX received another contract from NASA for $1.6 billion.
I messed up the first three launches, the first three launches failed. Fortunately the fourth launch – that was the last money that we had – the fourth launch worked, or that would have been it for SpaceX. But fate liked us that day
Elon Musk, CEO of SpaceX
Achievements
- ISRO – With the success acquired from the Polar and Geostationary launch vehicles (PSLVs and GSLVs), India decided to take their space exploration to the next level. The first mission to the moon in 2008 – Chandrayaan 1, a small robotic spacecraft into lunar orbit mounted on a modified PSLV. It surveyed the surface of the moon to locate the resources in greater detail. In 2014, India’s first interplanetary mission to the planet Mars known as Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) or Mangalyaan was launched. On 24 September 2014, it reached the Mars orbit which made India the first country in the world to place a spacecraft into the Martian orbit in its very first attempt. In between all these successes, ISRO also faced some discrimination.
Do you remember New York Times mocking India?
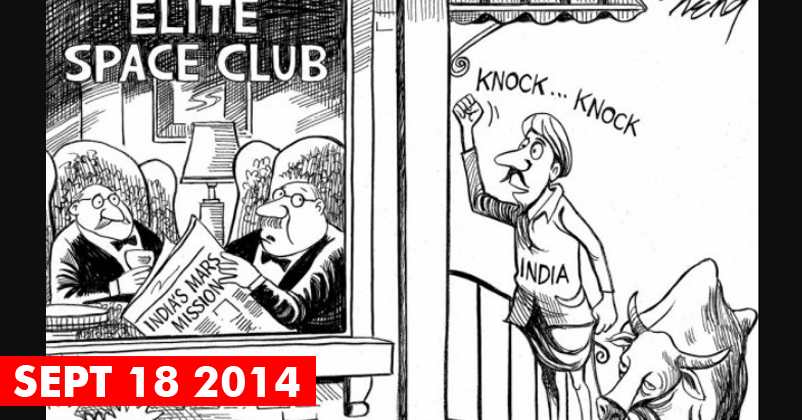

In 2014, NYT mocked India’s Mangalyaan achievement by publishing a cartoon which showed a rural Indian with a cow, standing outside the cabin of “Elite Space Club” and knocking its door. However, NYT apologised for the cartoon after Indians trolled them so aggressively.
To hush exclamation, on 18 December 2014, India launched GSLV Mk-III, the first experimental flight of ISRO’s heaviest and upgraded rocket vehicle from Sriharikota. On 15 February 2017, ISRO successfully launched 104 satellites using a single rocket from Sriharikota Space Centre; which is still one of the mind-blowing launches in history. Later in 2019, Chandrayaan-2 was the most complex mission ever attempted. Even though this mission ended in failure where ISRO lost the contact when the spacecraft was at 2.1km (1.3 miles) from the lunar surface, the mission holds the record of reaching the farthest and darkest area in the moon’s surface.
- SpaceX – In 2008, the Falcon 1 was the first privately developed liquid fuel rocket to reach Earth orbit. Moving on to next level, the SpaceX Dragon became the first private spacecraft in history to visit the space station. On December 21, 2015, the Falcon 9 rocket delivered 11 communications satellites to orbit. The first stage returned and landed at Landing Zone 1 making it the first-ever orbital class rocket landing. On April 8, 2016, the Falcon 9 rocket launched the Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station, and the first stage returned and landed on the “Of Course I Still Love You” droneship. On March 30, 2017, SpaceX achieved the world’s first reflight of an orbital class rocket. Following delivery of the payload, the Falcon 9 first stage returned to Earth for the second time. On February 7, 2018, Falcon Heavy made its first launch to orbit, successfully landing 2 of its 3 boosters and launching its payload to space. On May 21, 2020, the SpaceX became the first private company to take humans to the International Space Station on the SpaceX Crew Dragon. Do read the below article for more info.
Also Read – Welcome Back SpaceX Crew Dragon – A New Step towards MARS
Funding
Like I’ve mentioned already, both agencies are very cautious about their expenses. The government of India has allocated an approx of $90.94 billion every year which is approximately 14 times lesser than the NASA’s annual budget. SpaceX, on the other hand, operated on roughly $1 billion of funding, of which about $200 million was private funding ($100 million from Elon and $100 million from other investors) and $400-500 million from NASA.
The Idea of Reusability and Cost-efficiency
With limited access to funds, SpaceX and ISRO have always taken care of being highly cost-effective. The outcome of this is clearly visible in their approach towards reusability and result-oriented. Reusable Launch Vehicle – Technology Demonstration Program (RLV-TD) and Two Stage To Orbit (TSTO) are two approaches by ISRO to attain cost-efficiency which was tested successfully in the year 2016. SpaceX has its Reusable launch system development program for an orbital launch system that may be reused many times in a manner similar to the reusability of aircraft. SpaceX being an 18-year-old company has completed 92 total launches out of which 37 rockets were reflown ones.
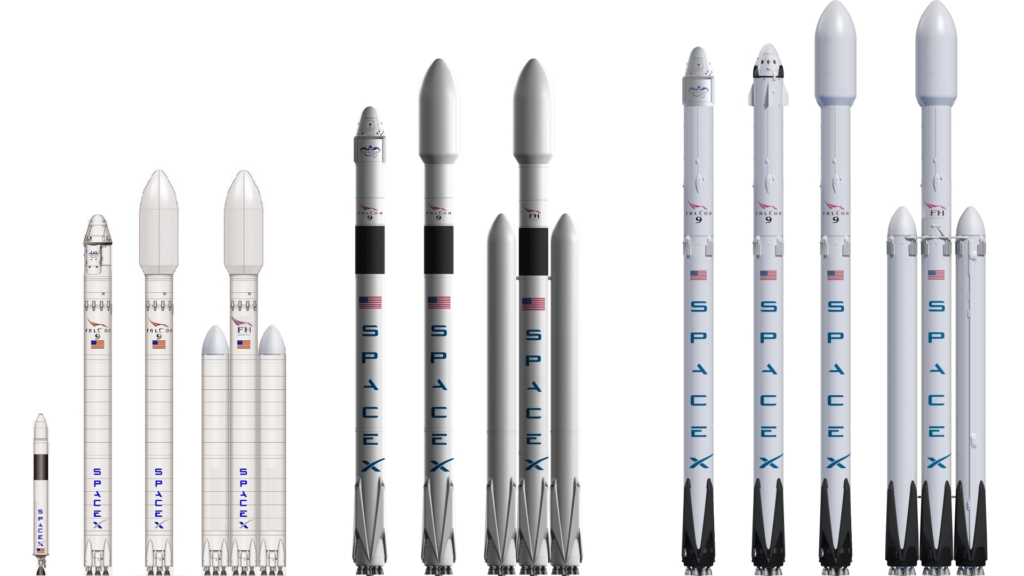
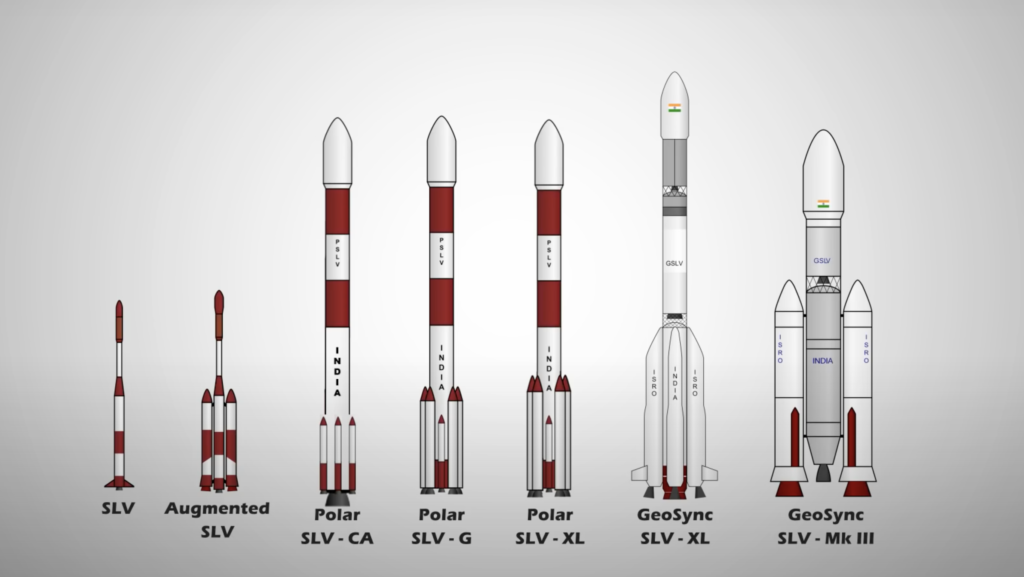
Launch Vehicles
SpaceX and ISRO are neck to neck, be it the technology or the looks of their launch vehicles. Another astonishing fact is that, both the space agencies have the capability and capacity to accommodate customer requirements in a very efficient way. This is evident in the images given below, where you can see variety of launch vehicles for both Polar and Geo levels.

trending articles right now
What are your thoughts on this? Let us know in the comment section below.
Stay tuned and stay updated to JUST A LIBRARY for the historic update.









